Blog
Signature Lawn and Landscape LLC
What is a Switching Power Supply and How Does It Work?
In today's fast-paced world, the role of a Switching Power Supply (SPS) is crucial. Experts emphasize its importance in various applications, from consumer electronics to industrial machinery. Dr. Emily Tran, a renowned electrical engineer, states, "Switching Power Supplies are the backbone of modern electronic systems." This highlights their fundamental position in powering devices efficiently.
Understanding how a Switching Power Supply operates can be complex. It involves intricate processes of voltage conversion and power regulation. Many users still don’t grasp its significance fully. Some view the SPS as just another component, missing its capacity to enhance energy efficiency and reliability. Details about its functionality can often lead to misunderstandings and confusion.
The design and implementation of a Switching Power Supply require careful consideration. Shortcomings in design can lead to inefficiencies and reliability issues. As technology advances, questions arise about how to improve these systems. The importance of ongoing research in SPS technology cannot be overstated. In the quest for better solutions, reflection on current practices is vital.
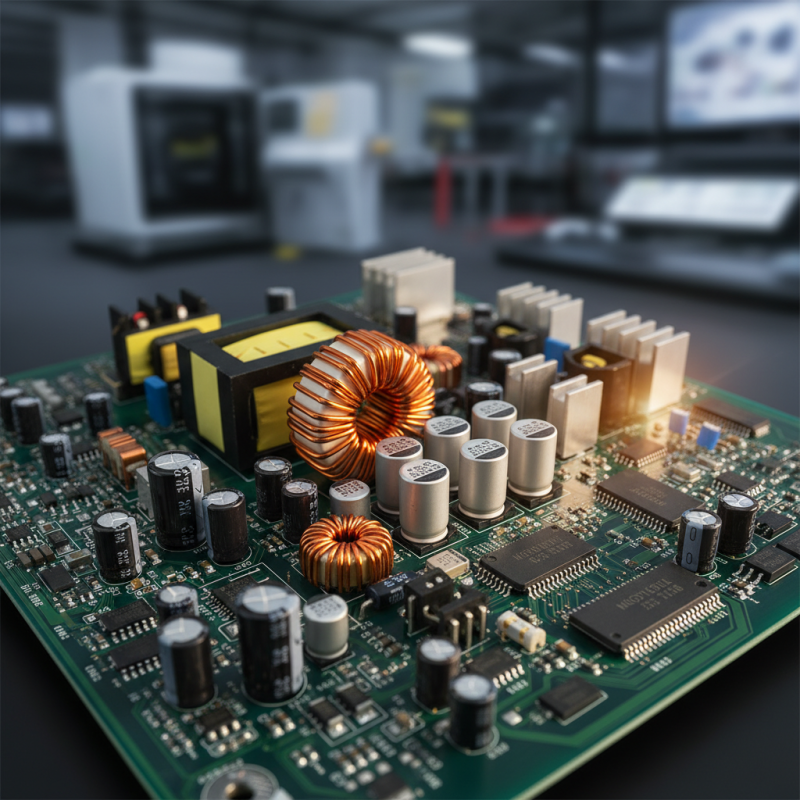
What is a Switching Power Supply?
A switching power supply (SPS) is a crucial component in modern electronics. It converts electrical energy efficiently. Unlike linear power supplies, SPS uses high-frequency switching. This method reduces energy loss and improves performance. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global switching power supply market is expected to reach $60 billion by 2025. This reflects its growing importance across various sectors.
One significant feature of SPS is its ability to handle varying loads. It adjusts output voltage automatically. This flexibility suits diverse applications, from computers to industrial machinery. However, not all designs are flawless. Some SPS may generate electromagnetic interference (EMI). This issue requires careful design considerations. Data from the International Electrotechnical Commission highlights that over 30% of electronic failures are linked to power supply issues. Thus, proper engineering is key.
While SPS is beneficial, there are challenges. Their complexity can lead to increased failure rates. Additionally, the manufacturing process must adhere to strict regulations. Some manufacturers might not comply fully, contributing to reliability issues. The need for continuous innovation in SPS design is apparent to meet evolving technology demands.
Key Components of a Switching Power Supply
A switching power supply is a crucial component in today's electronic devices. Its efficiency largely depends on its key components. The main parts include transformers, inductors, capacitors, and switching devices like transistors. Each component has a unique role that influences the power supply's overall performance.
Transformers, for example, convert voltage levels. They balance current in a way that maximizes energy transfer. Inductors store energy temporarily and help regulate current flow. Capacitors filter out noise and stabilize voltage. However, these components must be carefully selected. Incorrect choices can lead to inefficiency.
The design must consider the heat generated during operation. High temperatures can affect the lifespan of components. Regular maintenance and oversight are crucial. Sometimes, overlooked details can result in failures. Every component's quality affects the overall power supply. Therefore, reflection on design choices and material quality is essential for reliability.
The Working Mechanism of Switching Power Supplies
Switching power supplies are essential components in modern electronics. They convert electrical energy efficiently using a method called pulse-width modulation. This process allows the power supply to adjust voltage levels and maintain output stability.
The working mechanism involves several key components. A transformer converts the input voltage into a high-frequency signal. This signal is then rectified to smooth out the output. Control circuits monitor and adjust the voltage continuously. It’s interesting how small changes in the circuit can lead to fluctuations.
Challenges arise in maintaining efficiency and heat management. A poorly designed supply may generate excess heat. This can lead to reduced lifespan and reliability issues. Engineers must consider these factors while designing. Balancing efficiency with cost-effectiveness can be tricky. Ideal designs are always a work in progress.
What is a Switching Power Supply and How Does It Work?
| Parameter | Description | Typical Values |
|---|---|---|
| Input Voltage | The voltage supplied to the power supply unit. | 100-240 VAC |
| Output Voltage | The voltage delivered to the load after conversion. | 5V, 12V, 24V, etc. |
| Efficiency | Ratio of output power to input power, indicating performance. | 80-95% |
| Switching Frequency | Frequency at which the power supply switches the input voltage on and off. | 20 kHz to 1 MHz |
| Common Applications | Devices and systems that utilize switching power supplies. | Computers, TVs, LED lighting, and chargers |
| Form Factor | Physical size and shape of the power supply unit. | ATX, Mini, Open Frame |
Advantages of Using Switching Power Supplies
Switching power supplies are becoming more common in various applications. They offer distinct advantages that enhance efficiency and performance. One key benefit is their compact design. Unlike traditional linear power supplies, switching supplies are smaller and lighter. This feature allows for space-saving in devices where every inch counts.
Efficiency is another major advantage. Switching power supplies can convert a wide range of input voltages while maintaining high efficiency. Typically, they operate at about 80-90% efficiency, which is significantly better than linear counterparts. However, this efficiency can vary depending on the load conditions. When not properly managed, heat generation might become an issue, requiring additional cooling measures.
Flexibility is also noteworthy. These supplies can easily handle different output voltages, making them suitable for diverse applications. They can adapt to emerging technology needs without extensive redesigns. Yet, designing a switching power supply requires precise calculations. Mistakes can lead to undesirable outcomes like voltage spikes or electromagnetic interference. Balancing these factors is crucial for optimal performance.
Advantages of Switching Power Supplies
Common Applications of Switching Power Supplies
Switching power supplies are crucial in modern electronics. They efficiently convert electrical power for various applications. One common use is in computers. They provide stable power to the CPU and other components. This stability is essential for performance and reliability.
Another application is in consumer electronics. Devices like smartphones and tablets rely on these power supplies. They fit compactly into small devices. Switching power supplies can handle different voltages, making them versatile. However, the design can be complex. Sometimes, overheating occurs if not properly managed.
In industrial settings, these power supplies power machinery. They must endure harsh environments. A failure can halt operations. Thus, testing and quality control are vital. Ensuring reliability in this context is critical. Drawing lessons from these challenges can lead to better designs in the future.

Share On: